Database management system (DBMS ) practical file
Aim->To understand the basic concepts of RDBMS
SQL->standerd for structure query language it is a
standard language it is dealing with reletional database basically it is query
language for store in reletional database intially we are say squeal but after
1986 we call it SQL
Characteristics of SQL
1)
It is easy to learn
2)
It is use to access the data from reletional
database
3)
It can execute query such as creating the table
manuplating, updating, deleting, inserting
4)
It is also allows the user to set permission on
the table
Advantage of SQL
1)
High speed->user can quickly and efficiently
retrieve a large amount of records from a database.
2)
No coding needed->it is very easy to manage
the database system. It doesn’t require a substantial amount of code to manage
the database system.
3)
Well defined standards->the SQL databases
that are being used by ISO and ANSI.
4)
Portability->can be used in laptop, PCs,
server and even some mobile phones.
5)
Interactive language->SQL is a domain
language used to communicate with the database.
6)
Multiple data view->the users can make
different views of the database structure.
*important*
Row-> is called tupple
Column-> is called attribute
E.F.
code-> code discovered reletional database for mysql,orcal,ms access,IBM
supports RDBMS
Type of SQL statement-> 1)DML(stands for Data
Manipulation Language) is used for accessing and manuplating data in a database
The Commands which lies in DML
·
Insert->create a new record
·
Update->it modify the record
·
Delete->delete record
2)DDL(Stand for Data Definitions Language)->used by the
DBA and database designers to specify the conceptual schema of a database
The commands which lies in DDL
·
Create->create a database
·
Alter->modify the exist in table
·
Drop->deleting the entire table
DCL(Data Control
language)->the language use to control the acess of the data store in the
database the opretions include previleges that can be branded two statement
•grant->(giving
the permission) giving the
privilege to acess the •revoke->
means taking the permission previlege
DQL(Data Query language)->it is language retrieving data
from the database
·
Select-> retrieving data
TCL(Transaction Control Language)-> is language use for
transaction
Commands
·
Comite->command is used to permanently save
any transaction into the database.
·
Rollback->command is used to restore the
database for the last committed state.
·
Savepoint->command is used to temporarily
save a transaction so that you can roll back to that point whenever necessary.
The term use in reletional database
·
Stable or reletion->collection of row and
column
·
Record or tupple->each row in database is record
·
Column->column name specify the vertical
entity with respect which information is column
·
Domain->it is a set of permitted value for an
attribute in a table
·
Instance or schema->it describe the structure
of the table at database.
·
Schema-> overall design of database this is
unique key identifier for any table
è
Customer table
|
Customer |
City |
Country |
|
Manoj |
Gurugram |
India |
|
Rahul |
Bhiwani |
India |
Oracal
is most pormink RDBMS develop 1977 till different versions release
Practical 2
Aim:-To perform basics SQL commands
SQL data types
·
String->1)char->it store string values cantaining
any character in a character set.
2) Varchar->it store string values
containing any characters in a character setset but of variable length
3)BLOB-> it store binary strings in hexa
decimal format (for large values)
·
Number->1)int->it store exect numbers with
a predefine presigen
2)temporal->it used to store the time
stamp values
·
Boolean->true and false
·
Varchar2->string and number both sports.
Create->purpose the create table cammand is used to
create a new table in the database
*1)Create table table name
(column name data type (size),
Column name data type (size),column name data type (size));
example
Create table student(
Name varchar2(21),
Rollno varchar2(8),
Address varchar2 (20));
*2) Insert into-> the insert in to statement (commands)
in sql is used to insert a new row in table.
Insert into table name values(value 1, value 2, value 3);
Example->1st row-> insert into student values(‘rohit',210104,’sec-55’);
2ndrow-> insert into student values (‘raj’,210105,’sec-47’);
*1)Select statement->the select command is used to
retrieve the data from the database
Example->select*from student;
*2)fetch specific column
Select column1, column 2 from table name;
Practice->table name->client
|
Client no. |
Name |
Address1 |
Address2 |
City |
Pincode |
State |
Balance due |
|
C0001 |
Ajay |
Thomash
street |
Pawai |
Mumbai |
122004 |
Maharashtra |
1500 |
|
C0002 |
Ram |
Vigyan street |
Pukter |
Jaipur |
122011 |
Rajasthan |
1600 |
|
C0003 |
Anil |
Dayal street |
Rohin |
Delhi |
123022 |
Delhi |
2000 |
|
C0004 |
Rashmi |
Gelf course |
Extension |
Gurgaon |
122001 |
Haryana |
4000 |
|
C0005 |
Ankit |
Auring street |
Shastri Nagar |
Meerut |
122051 |
Utarperdesh |
4500 |
Input
code
Create table client (clientno varchar2(5),name
varchar2(10),address1 varchar2(20),address2 varchar2(10),city
varchar2(15),pincode int,state varchar2(20),balancedue int);
Insert into client values('c0001 ','ajay','thomash street','pawai','mumbai',122004,'maharatra',1500);
Insert into client values ('c0002 ','ram','vigyan street','pukter','jaipur',122011,'rajesjthan',1600);
Insert into client values ('c0003 ','anil','dayal street','rohin’,’delhi’,123022,’delhi’,2000);
Insert into client values (‘c0004’,’rashmi’,’gelf course’,’extension’,’gurgoan’,122001,’haryana’,4000);
Insert into client values (‘c0005’,’ankit’,’auring
street’,’shastrinagar’,’meerut’,122051,’uterpardesh’,4500);
Output code
Select*from client;
**Where clause-> the where clause is used to filter the
records basically it is used to extract only those records that full filled a
specified condition
Example-> select column1, column 2,...
From table name
Where condition;
**What condition**
Operator Discription
=. Equal
to
> Greater than
<. Less than
>=. Greater than
or equal to
<=. Less than or
equal to
!=. Not equal to
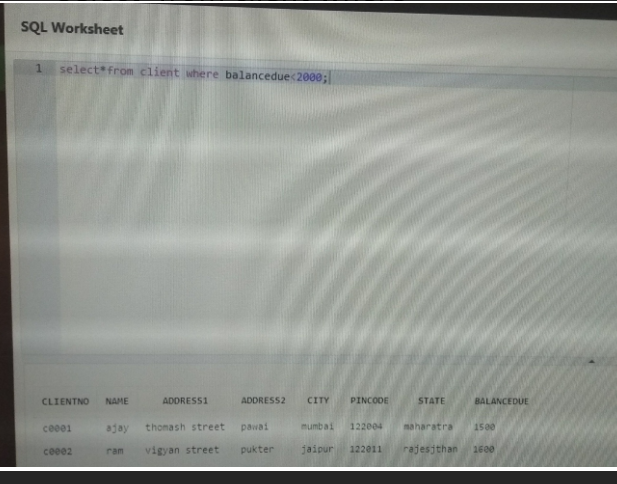
Q1 display all the records where balancedue is less than
2000
Select*from client where balancedue<2000;
Practical 3
Aim-> To understand the basic of SQL oprators (AND,OR,NOT)
1.
SQL AND-> oprator displays a records if all
the conditions separated by AND are true syntax:- select column1 ,column2
From table name
Where condition1 AND condition2 AND
conditionn;*note:-AND if both condition are true then this is true otherwise
not be true
2.
SQL OR-> the SQL OR oprator displays a record
if any of the condition seprated by OR is true
3.
Syntax:- select column1 ,column2
From table name
Where condition1AOR condition2 OR
conditionn; *Note-> OR if both condition falls then OR falls otherwise this is not be falls
4.
SQL NOT-> the NOT oprator displays a records
if the condition is not true
Syntax:- select column1, column2
From table name
Where NOT condition;
Create table customer (customerid
int,customerName varchar2(10),contctName varchar2(10),address varchar2(10),city
varchar2(10),postalcode int,country varchar2(10));
Insert into customer
values(1,’alfreds’,’maria’,’obere’,’berlin’,12209,’germany’);
Insert into customer
values(2,’ana’,’wistom’,’avda’,’maxico’,1245,’mexico’);
Insert into customer
values(3,’antonio’,’joph’,’mataden’,’maxico’,1245,’mexico’);
Insert into customer
values(4,’horn’,’rane’,’honas’,’london’,1409,’uk’);
Insert into customer
values(5,’bergul’,’mofin’,’bergun’,’lulea’,1502,’sweden’);
Insert into customer
values(6,’baunder’,’maje’,’foston’,’mannheim’,1600,’germany’);
Insert into customer
values(7,’tim’,’lafin’,’konom’,’strasbourg’,1800,’france’);
Insert into customer
values(8,’gilm’,’toson’,’jonsom’,’madrid’,1400,’spain’);
Input for AND
Select*from customer
Where country=’germany'and
city='berlin';
Input of OR
Select*from customer
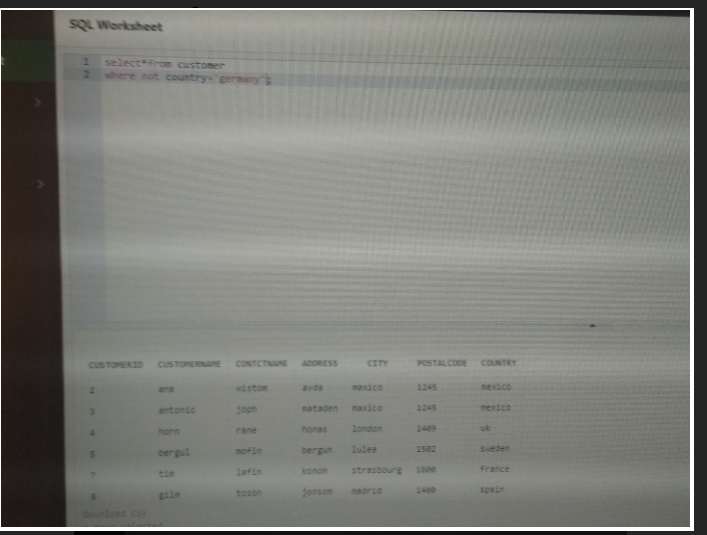
Input of NOT
Select*from customer
Where not country=’germany’;
Input of AND/OR both
Select*from customer
Where
country=’germany’and(city=’berlin’or city=’munchen’);
Practical 4
Aim-> To perform lab exercise
on the unary operators (select and project)
Theory->1) select -> the
first operater is the select oprator the select oprator is used to choose the
subject of the tupple from reletion that satisfy a given condition
2)Project-> the project is
used to select certain columns from the table and discart rest of the column
basically with the help project we carry out vertical partition
This is by sql
Project->eliminates columns
Select-> eliminates rows.
Create employee table
create table employee (employeeid
int,employeeName varchar2(10),departmentName varchar2(10),salary int);
insert into employee
values(10101,'srinivas','mechanical',65000);
insert into employee
values(10102,'arjun','it',64000);
insert into employee values(10103,'ram','hr',70000);
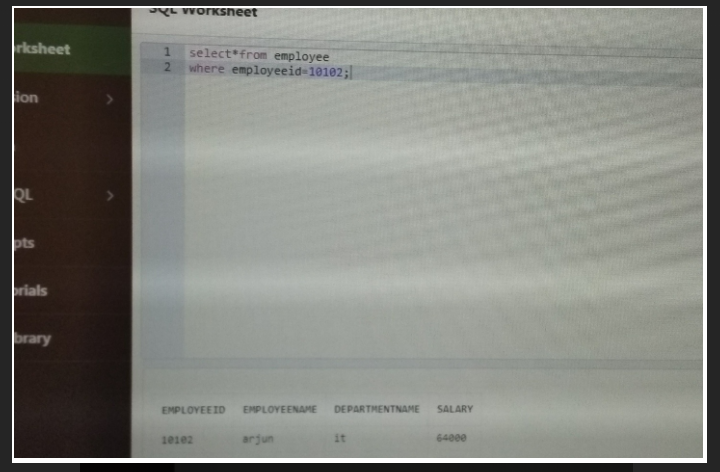
Query1->select*from employee
where employeeid=10102;
from employee
where employeeid=10102;
where salary=64000 and
departmentname='it'
create table instructors (Name
varchar2(10),department varchar2(10),salary int);
insert into instructors
values('anuj','physics',90000);
insert into instructors
values('ram','mechnical',75000);
insert into instructors
values('sahil','science',80000);
insert into instructors
values('ankit','math',50000);
insert into instructors
values('shruti','dames',60000);
| Query 2->select*from instructors |
where salary>80000;
Query 3->select*from instructors
where salary>60000 and
department='physics';
where department='mechnical';
create table customer (customerid
varchar2(10), Name varchar2(10),city varchar2(10));
insert into customer
values('c10100','steve','agra');
insert into customer
values('c10111','raghu','agra');
insert into customer
values('c10115','charu','noida');
insert into customer
values('c10117','ajeet','delhi');
insert into customer
values('c10118','carl','delhi');
Query2->select name,city
from customer;
insert into student values(1,'aman',20);
insert into student values(2,'atul',20);
insert into student values(3,'baljeet',20);
insert into student values(4,'harsh',20);
insert into student values(5,'prateek',20);
insert into student values(6,'pratham',20);
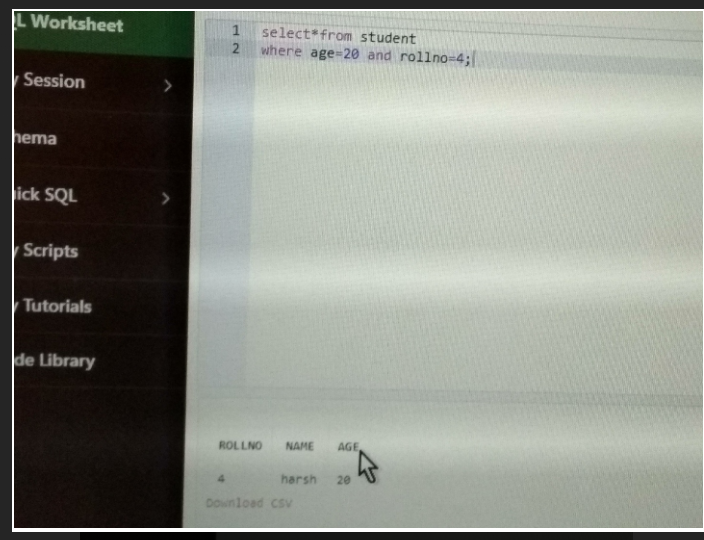
where age=20 and rollno=4;
from student;
Aim->To perform the basic sql commands:-
1)
Order by->In the sql order by clause is used to short the
data in ascending or descending order base on one or more column the basic
syntax of the order by->
Select column list
From table name
Where condition
Order by column1..columnN;
By default order by clause is
always ascending order
But if you want to decreasing
order then the order by desc;
2)
Distinct-> the select distinct command is
used to return only the distinct values (distinct mean different values) in
order to remove duplicate values be applie the distinct command
Syntax of distinct command
Select distinct column1,...columnN
From table name;
**Creating employees table**
create table employees(id int,name
varchar2(10),age int,address varchar2(10),salary int);
insert into employees
values(1,'ramesh',32,'ahmedabad',2000);
insert into employees
values(1,'khilan',25,'delhi',1500);
insert into employees
values(1,'khaushik',23,'kota',2000);
insert into employees
values(1,'chitali',25,'mumbai',6500);
insert into employees
values(1,'hardik',27,'bhopal',8500);
insert into employees
values(1,'komal',22,'mp',4500);
insert into employees values(1,'muffy',24,'indore',9000);
insert into employees
values(1,'muffy',23,'chennai',2100);
| Query 1->select salary |
from employees
order by salary;
from employees;
where address='indore';
from employees
where salary>2000;
where name='ramesh'or
name='khilan';
where address!='bhopal';
Aim-> To implement the concept
of joins in sql 1)inner join 2) outer join
Basic introduction-join
-inner join and its types
-outer join and its types
Join->A JOIN clause is used to
combine rows from two or more tables, based on a related column between them.
Inner join->
records that have matching values in both tables
Left outer join-> all records from the left table,
and the matched records from the right table
Right outer join-> Returns all records from the
right table, and the matched records from the left table
Full outer join->Returns all records when there is
a match in either left or right table
Create table1->create table orders ( orderid int,
customerid int, orderdate varchar2(10));
insert into orders values(10308,2,'18-9-21');
insert into orders values(10309,37,'21-10-21');
insert into orders values(10310,77,'1-01-21');
insert into customer values(1,'alex','maria','germany');
insert into customer values(2,'frido','helen','mexico');
insert into customer values(3,'thomas','rose','mexica');
FROM Orders
INNER JOIN Customer
ON Orders.CustomerID=Customer.CustomerID;
FROM Orders
left join Customer
ON Orders.CustomerID=Customer.CustomerID;
FROM Orders
right join Customer
ON Orders.CustomerID=Customer.CustomerID;
FROM Orders
full join Customer
ON Orders.CustomerID=Customer.CustomerID;
Aim-> write the sql queries to amplement lab exercise-joins
Create table employee (employeeid int,fname varchar2(10),lname
varchar2(15),age int, phoneno int, address varchar2 (20));
Insert into employee values(1,'vardhan','kumar',22,9812467899,'delhi');
Insert into employee
values(2,'himani','sharma',32,9814126771,'mumbai');
Insert into employee
values(3,'aayushi','shresth',24,9991261721,'kolkata');
Insert into employee values(4,'hemanth','sharma',25,9996172121,'banglore');
Insert into employee
values(5,'sewathi','kapoor',26,9812161712,'hydrabad');
Create table projects (projectid int, employeeid int, clientid int,
projectname varchar2 (4));
Insert into projects values (111,4,3,'p1');
Insert into projects values (222,2,1,'p2');
Insert into projects values (333,3,5,'p3');
Insert into projects values (444,3,2,'p4');
Select employee.employeeid, employee.fname, employee.lname,
employee.age, employee.phoneno, employee.address, projects.projectid,
projects.clientid, projects.projectname
From employee
Inner join projects on employee.employeeid=projects.employeeid;
Select employee.employeeid, employee.fname, employee.lname,
employee.age, employee.phoneno, employee.address, projects.projectid,
projects.clientid, projects.projectname
From employee
Left join projects on employee.employeeid=projects.employeeid;
Select employee.employeeid, employee.fname, employee.lname,
employee.age, employee.phoneno, employee.address, projects.projectid,
projects.clientid, projects.projectname
From employee
Right join projects on employee.employeeid=projects.employeeid;
Select employee.employeeid, employee.fname, employee.lname,
employee.age, employee.phoneno, employee.address, projects.projectid,
projects.clientid, projects.projectname
From employee
Full join projects on employee.employeeid=projects.employeeid;
Aim->to implement the concept of constraints on the given table
using sql
1) NOT NULL Constraint->The not
null constraint enforces a column to NOT accept NULL values.
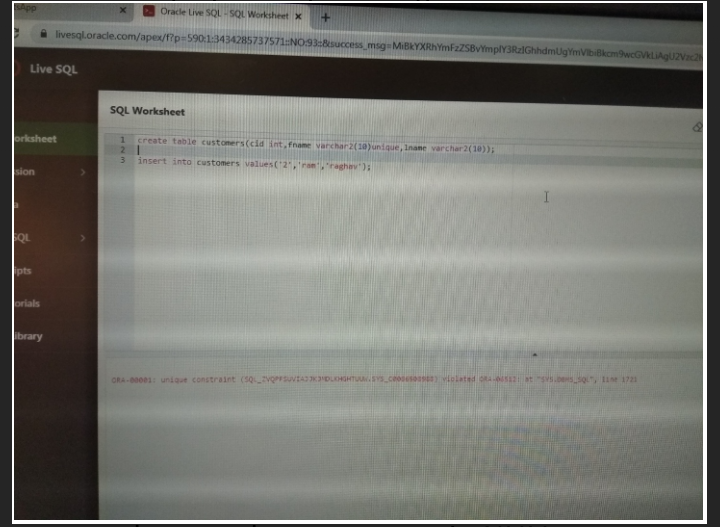
create table customers(cid int not
null,fname varchar2(10),lname varchar2(10));
insert into customers values('','ram','sony');
Create table customers(cid int,fname
varchar2(10)unique,lname varchar2(10));
insert into customers values('1','ram','suma');
insert into customers values('2','rahul','sony');
insert into customers values('3','rahul','shima');
create table emloyee(cid int primary key,fname
varchar2(10),lname varchar2(10));
insert into employee values('1','ram','raghav');
insert into customers values('1','shyam','jham');
insert into customers
values('','shyam','jham');
CREATE TABLE supplier
( supplier_id numeric(10) not null,
Supplier_name varchar2(50)
not null,
Contact_name varchar2(50),
PRIMARY KEY (supplier_id)
);
CREATE TABLE products
( product_id numeric(10) not null,
Supplier_id numeric(10) not
null,
FOREIGN KEY (supplier_id)
REFERENCES
supplier(supplier_id)
);
Insert into supplier values(1,’rohan’,’jony’,):
Insert into products values(101,1);
Insert into supplier values(2,’shyam’,’jony’);
Insert into products values(102,2);
Insert into supplier values(3,’shy’,’jha’);
Insert into products values(103,3);
Insert into products values(104,4);
create table person(pid int not null,fname
varchar2(10),lname varchar2(10), age int check(age>=18));
insert into person
values(1,'rohan','singh',17);
Practical 9
Aim-> to perform the basic SQL commands
udate, delete, alter,drop and truncate, between
1) SQL Update ->The
update statement is used to modify the existing records in a table.
Syntax:-UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1, column2 =
value2, ...
WHERE condition;
2)Alter->The alter table statement is used to add, delete,
or modify columns in an existing table.
Syntax:- Alter table table_name add column_name datatype(size);
a)alter delete-> delete a column
in a table
Syntax->
alter table table name
Delete column column name;
3) Between->The
between operator selects values within a given range. The between operator
is inclusive: begin and end values are included
Syntax:-select column_name(s) from table_name where column_name between value1
and value2;
4) Delete->The
delete statement is used to delete existing records in a table.
Syntax:- delete from table_name;
Delete the specific row from the table
Syntax:- delete
from table_name where condition;
5)Drop->The
drop table statement is used to remove an existing table in a database.
6) truncate->A truncate SQL
statement is used to remove all rows (complete data) from a table.
Syntax:- truncate table tablename;
Create employee table
create table employee(eid int,ename varchar2(12),age
int, city varchar2(20),salary int);
insert into employee values(1,'ramesh',32,'ahmedabad',2000);
insert into employee
values(2,'khilan',25,'delhi',3000);
insert into employee
values(3,'khaushik',26,'bangalore',4000);
insert into employee values(4,'chitali',32,'chennai',5000);
insert into employee
values(5,'hardik',31,'gurugram',2000);
insert into employee
values(6,'komal',27,'idore',1000);
insert into employee
values(7,'muffy',28,'bhopal',3000);
Query 1
update employee
set ename='ramesh gupta',
city='delhi'
where eid=1;
select* from employee;
Query 2
update employee
set age=29
where salary=4000;
select*from employee;
alter table employee
add phoneno number(10);
select*from employee;
update employee
set phoneno=9823123423
where eid=1;
update employee
set phoneno=9323123425
where eid=2;
update employee
set phoneno=9873124523
where eid=3;
update employee
set phoneno=9853723423
where eid=4;
update employee
set phoneno=9824123421
where eid=5;
update employee
set phoneno=9626123423
where eid=6;
update employee
set phoneno=9823523426
where eid=7;
Select*from employee;
create table department(eid
int,ename varchar2(10),department varchar2(10),contactno number(10));
insert into department
values(101,'isha','e101',9817127844);
insert into department
values(102,'priya','e104',9887127544);
insert into department
values(103,'neha','e105',9887137554);
insert into department
values(104,'rahul','e102',9847337554);
insert into department values(105,'abhishek','e101',8787337554);
Query 4
SELECT*from department
where department='e104'
or
department='e102';
Query 5
update department
set ename='isha yadav'
where eid=101;
select*from department;
Query 6
delete from department
where ename='abhishek';
select*from department;
alter table department
add departmentname varchar2(10);
update department
set departmentname='cse'
where department='e101';
update department
set departmentname='me'
where department='e102';
update department
set departmentname='ba'
where department='e104';
update department
set departmentname='ec'
where department='e105';
select*from department;
Aim->To perform the explanation
of the following concepts
A)
Mysql,
Oracle,Db2,sql server
B)
Instruction
deletion,sql server injection
MySQL
is a widely used relational database management system (RDBMS).MySQL is free
and open-source.MySQL is ideal for both small and large applications.
- Use of my
sql->MySQL
is very fast, reliable, scalable, and easy to use
- MySQL
is cross-platform
- MySQL
is compliant with the ANSI SQL standard
- MySQL
was first released in 1995
- MySQL
is developed, distributed, and supported by Oracle Corporation
- MySQL
is named after co-founder Monty Widenius's daughter: My
Orcal->Oracle database is a relational database
management system. It is also called OracleDB, or simply Oracle. It
is produced and marketed by Oracle
Corporation. It
was created in 1977 by Lawrence Ellison and other engineers. It is one of the
most popular relational database engines in the IT market for storing,
organizing, and retrieving data.
Use->Oracle
database manages data with the help of an open, complete, and integrated
approach. The following are features that complete the demand for powerful
database management:
Availability: It is never offline or out of service
that means supported 24*7 availability of the database.
Security: Oracle has a mechanism for controlling
and accessing the database to prevent unauthorized access.
Scalability: It provides features like RAC (Real
Application Cluster) and Portability, which makes an Oracle database scalable
based on usage.
Performance: Oracle provides performance optimization
tools such as Oracle Advanced Compression, Oracle Database In-Memory, Oracle
Real Application Testing, and Oracle Times Ten Application-Tier Database Cache.
Their main objective is to improve system performance to the highest possible
level.
Management: Oracle Multitenant is a
database management tool that combines a single container database with many
pluggable databases in a consolidated design.
DB2-> DB2 is a database server developed by IBM. It is a Relational
Database Management Syatem which is designed to store, analyze and retrieve the
data efficiently.
DB2 database supports
Object Oriented features and non relational structure with XML.
Use-> DB2 Server, which can run on any authoritative
operating systems such as Linux, UNIX, and Windows.
SQL-> is a short-form
of the structured query language, and it is pronounced as S-Q-L or sometimes as
See-Quell.
This database language
is mainly designed for maintaining the data in relational database management
systems. It is a special tool used by data professionals for handling
structured data (data which is stored in the form of tables). It is also
designed for stream processing in RDSMS.
Use->1.NOprogramming
needed SQL does not require a large number of coding lines for managing the
database systems.
2.High-SpeedQuery Processing
->
A large amount of data
is accessed quickly and efficiently from the database by using SQL queries.
Insertion, deletion, and updation operations on data are also performed in less
time.
3. Standardized Language->
SQL follows the long-established standards of
ISO and ANSI, which offer a uniform platform across the globe to all its users.
5. Portability-> The structured query language can be easily
used in desktop computers, laptops, tablets, and even smartphones.
6. Interactive language->We can easily learn and understand the SQL
language. We can also use this language for communicating with the database
because it is a simple query language.
The
SQL Injection-> is a code penetration technique that might cause loss to our
database. It is one of the most practiced web hacking techniques to place
malicious code in SQL statements, via webpage input. SQL injection can be used
to manipulate the application's web server by malicious users.
SQL injection generally
occurs when we ask a user to input their username/userID. Instead of a name or
ID, the user gives us an SQL statement that we will unknowingly run on our
database.
Intrusion detection->An
IDS is a security system which monitors the computer systems and network
traffic. It analyses that traffic for possible hostile attacks originating from
the outsider and also for system misuse or attacks originating from the
insider. A firewall does a job of filtering the incoming traffic from the
internet, the IDS in a similar way compliments the firewall security. Like, the
firewall protects an organization sensitive data from malicious attacks over
the Internet, the Intrusion detection system alerts the system administrator in
the case when someone tries to break in the firewall security and tries to have
access on any network in the trusted side.
Aim-> to perform SQL
like operator on relational tables
The LIKE operator is used in a WHERE clause to search for a
specified pattern in a column.
There are two wildcards often used in conjunction with the
LIKE operator:
- The
percent sign (%) represents zero, one, or multiple characters
- The
underscore sign (_) represents one, single character
Syntax->
select column1,column2
From
table name
Where
column like pattern;
Create
table student*
create table student(studentid int, sname
varchar2(10));
insert into student values(1,'akash');
insert into student values(2,'mitali');
insert into student values(3,'sanjay');
insert into student values(5,'sonali');
insert into student values(4,'anuj');
Query
1-> select*from student
where
sname
like 'a%';
Query
2->select*from student
where
sname
like '%i';
Query
3->select*from student
where
sname
like '%an%';
Query4->select*from
student
where
sname
like '_o%';
Query5->select*from
student
where
sname
like '__n%';
Query6->select*from
student
where
sname
like 'a__%';
Query7->select*from
student
where
sname
like 'm%i';
Aim->to perform the
aggregation function in sql
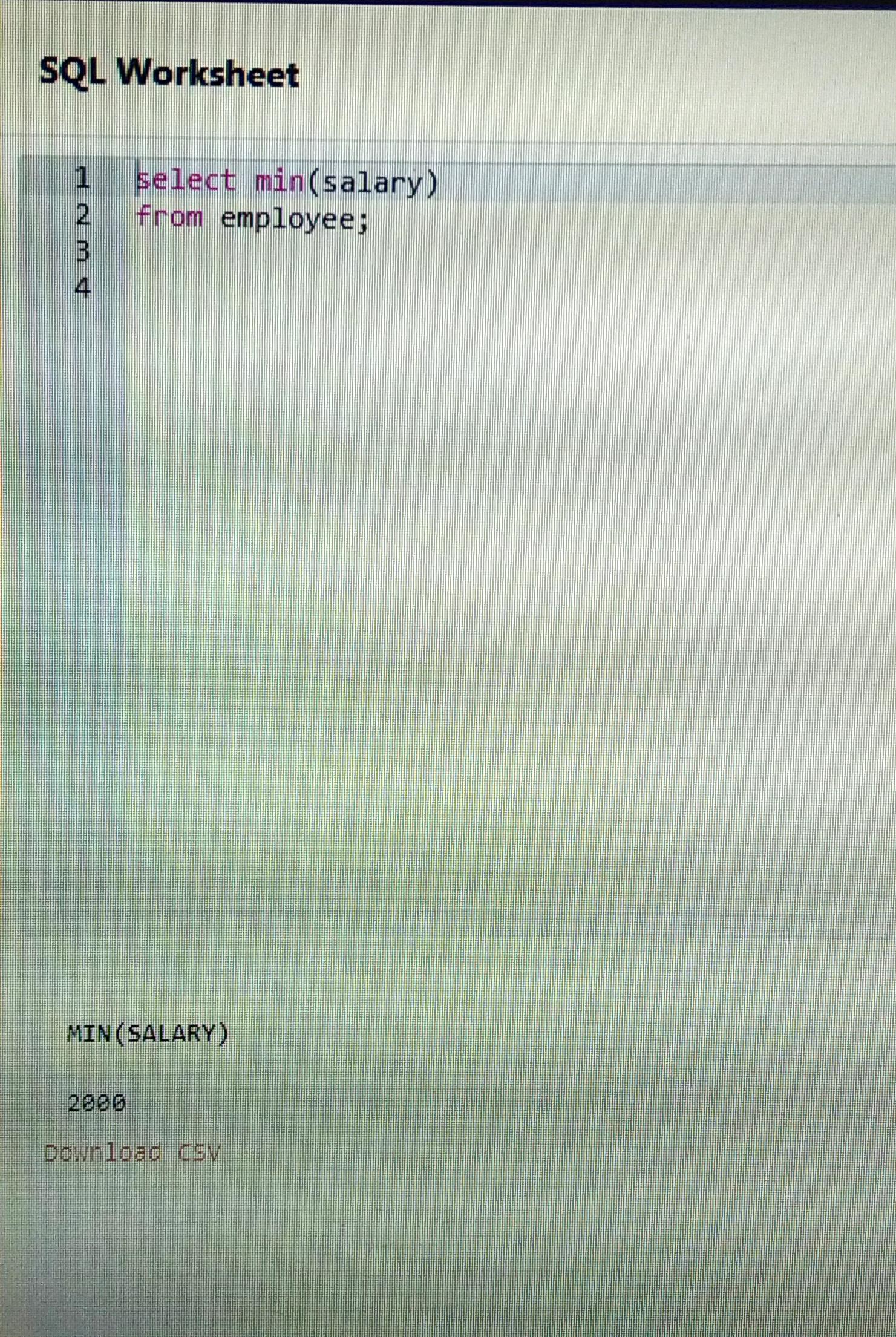
A)MIN()->The MIN() function returns
the smallest value of the selected column.
B)MAX()->The MAX() function returns
the largest value of the selected column.
C)COUNT()->
The COUNT() function returns the number of rows that matches a
specified criterion.
D)AVG()->The AVG() function returns
the average value of a numeric column.
E)SUM()->The SUM() function returns
the total sum of a numeric column.
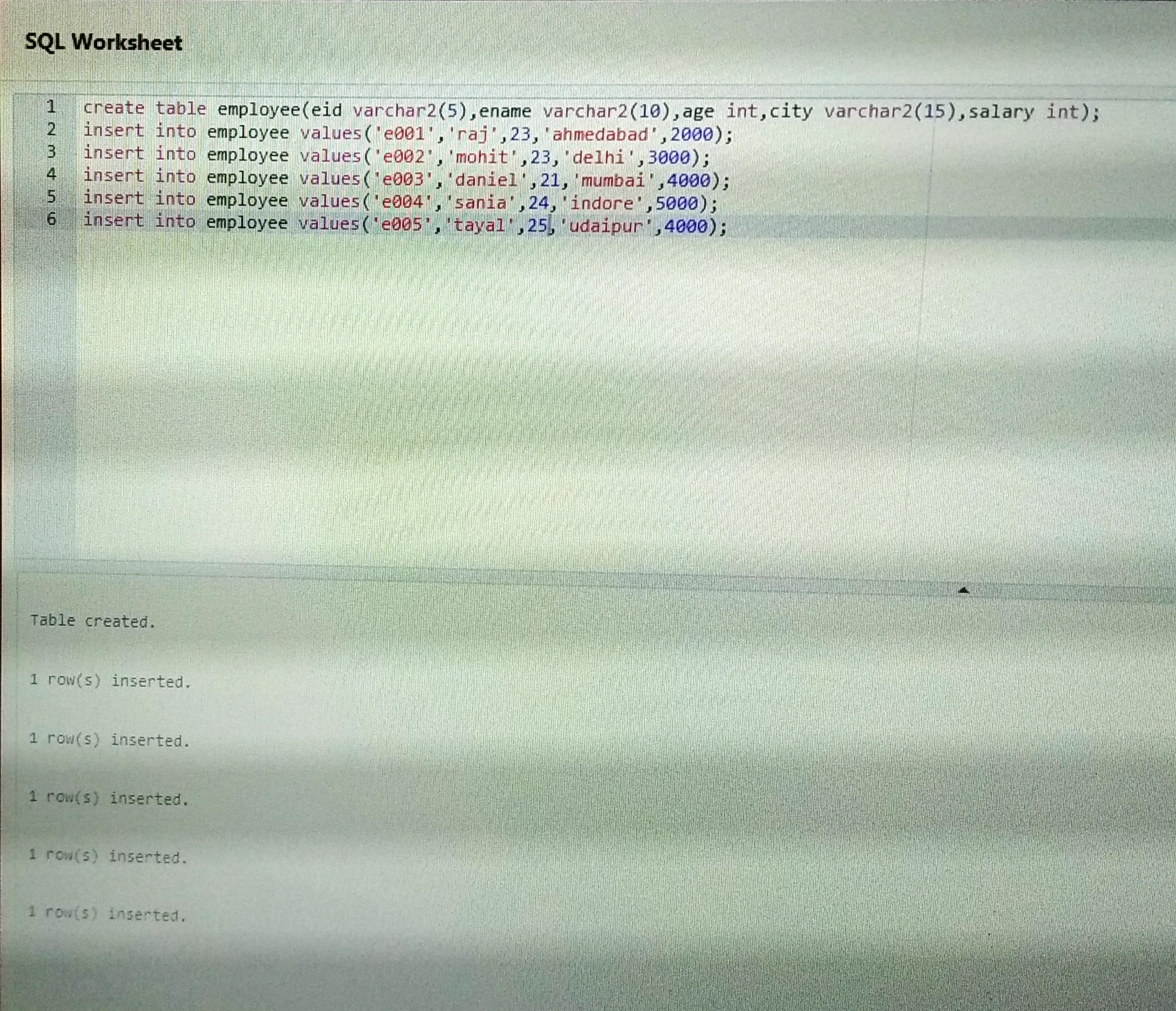
Create
table employee*
create
table employee(eid varchar2(5),ename varchar2(10),age int,city
varchar2(15),salary int);
insert
into employee values('e001','raj',23,'ahmedabad',2000);
insert
into employee values('e002','mohit',23,'delhi',3000);
insert
into employee values('e003','daniel',21,'mumbai',4000);
insert
into employee values('e004','sania',24,'indore',5000);
insert
into employee values('e005','tayal',25,'udaipur',4000);
from employee;
Query 2->select
max(salary)
from
employee;
Query 3->select
avg(salary)
from employee;
from
employee;
from
employee;
































































Comments
Post a Comment