Analysis and design of algorithms (ADA) lab practical file
Practical 1
Aim-> insertion/deletion from middle
Algorithm->step 1 start
Step2 if(newNode == NULL) {
cout<<("Unable to allocate memory.");
} else {
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next
= NULL; temp = head;
for(i=2;
i<=position-1; i++) {
temp = temp->next;
if(temp ==
NULL) break; }
if(temp !=
NULL) {
newNode->next = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;
cout<<("DATA INSERTED SUCCESSFULLY\n");
} else {
cout<<("UNABLE TO INSERT DATA AT THE GIVEN POSITION\n")
Step3 stop
Code-> #include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node { int
data;
struct node
*next;}*head;
void createList(int n);
void insertNodeAtMiddle(int data, int position);
void deleteMiddleNode(int position);
void displayList();
int main()
{ int n, data,
position;
cout<<("Enter the total number of nodes: ");
cin>>(n);
createList(n);
cout<<("\nData in the list \n");
displayList();
cout<<("\nEnter data to insert at middle of the list:
");
cin>>(data);
cout<<("\nEnter the position to insert new node: " );
cin>>(position);
insertNodeAtMiddle(data, position);
cout<<("\nData in the list \n");
displayList();
cout<<("\nEnter the node position you want to
delete: ");
cin>>(position);
deleteMiddleNode(position);
cout<<("\nData in the list \n");
displayList();
return 0;}
void createList(int n)
{ struct node
*newNode, *temp;
int data, i;
head = (struct
node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(head == NULL)
{ cout<<("Unable to allocate
memory.");
} else
{
cout<<("Enter
the data of node 1: ");
cin>>(data);
head->data
= data;head->next = NULL;temp = head;
for(i=2;
i<=n; i++) {
newNode =
(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(newNode
== NULL) {
cout<<("Unable to allocate
memory.");
break; } else
{
cout<<"Enter the data of
node"<<i<<":";
cin>>(data);
newNode->data = data;newNode->next = NULL;
temp->next = newNode; temp = temp->next; } }
cout<<("SINGLY LINKED LIST CREATED SUCCESSFULLY\n");
}}
void insertNodeAtMiddle(int data, int position)
{ int i;
struct node
*newNode, *temp;
newNode = (struct
node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(newNode ==
NULL) {
cout<<("Unable to allocate memory.");
} else {
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL; temp =
head;
for(i=2;
i<=position-1; i++) {
temp = temp->next;
if(temp ==
NULL) break; }
if(temp !=
NULL) {
newNode->next = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;
cout<<("DATA INSERTED SUCCESSFULLY\n");
} else {
cout<<("UNABLE TO INSERT DATA AT THE GIVEN POSITION\n");
} } }
void displayList()
{ struct node *temp;
if(head == NULL)
{ cout<<("List is empty.");
} else
{
temp = head;
while(temp !=
NULL)
{
cout<<"Data="<< temp->data<<"\n";
temp =
temp->next; } } }
void deleteMiddleNode(int position)
{ int i;
struct node
*toDelete, *prevNode;
if(head == NULL)
{ cout<<("List is already
empty.");
} else {
toDelete =
head; prevNode = head;
for(i=2;
i<=position; i++) {
prevNode =
toDelete; toDelete = toDelete->next;
if(toDelete == NULL)
break; }
if(toDelete !=
NULL)
{ if(toDelete == head)
head =
head->next; prevNode->next = toDelete->next;
toDelete->next = NULL;
free(toDelete);
cout<<("SUCCESSFULLY DELETED NODE FROM MIDDLE OF
LIST\n");
} else {
cout<<("Invalid
position unable to delete.");
} }}
Input
Output
Practical 2
Aim-> insertion/deletion from end
Algorithm-> step1 start
Step2 if(newNode == NULL)
{ cout<<("Unable to allocate
memory.");
} else
{
newNode->data
= data; // Link the data part
newNode->next = NULL;
temp = head;
while(temp !=
NULL && temp->next != NULL) temp = temp->next;
temp->next
= newNode;
cout<<("DATA INSERTED SUCCESSFULLY\n");
}}
Step3 stop
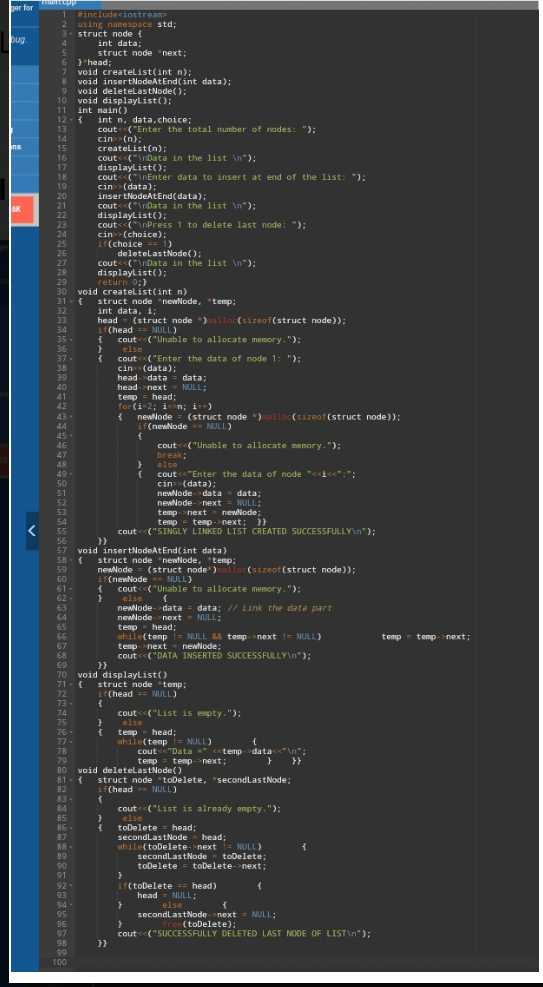
Code-> #include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
}*head;
void createList(int n);
void insertNodeAtEnd(int data);
void deleteLastNode();
void displayList();
int main()
{ int n,
data,choice;
cout<<("Enter
the total number of nodes: ");
cin>>(n);
createList(n);
cout<<("\nData in the list \n");
displayList();
cout<<("\nEnter data to insert at end of the list: ");
cin>>(data);
insertNodeAtEnd(data);
cout<<("\nData in the list \n");
displayList();
cout<<("\nPress 1 to delete last node: ");
cin>>(choice);
if(choice == 1)
deleteLastNode();
cout<<("\nData in the list \n");
displayList();
return 0;}
void createList(int n)
{ struct node
*newNode, *temp;
int data, i;
head = (struct
node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(head == NULL)
{ cout<<("Unable to allocate
memory.");
} else
{ cout<<("Enter the data of node 1:
");
cin>>(data);
head->data
= data;
head->next
= NULL;
temp = head;
for(i=2;
i<=n; i++)
{ newNode = (struct node
*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(newNode
== NULL)
{
cout<<("Unable to allocate memory.");
break;
} else
{ cout<<"Enter the data of node
"<<i<<":";
cin>>(data);
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
temp->next = newNode;
temp = temp->next; }}
cout<<("SINGLY LINKED LIST CREATED SUCCESSFULLY\n");
}}
void insertNodeAtEnd(int data)
{ struct node
*newNode, *temp;
newNode = (struct
node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(newNode ==
NULL)
{ cout<<("Unable to allocate
memory.");
} else
{
newNode->data = data; // Link the data part
newNode->next = NULL;
temp = head;
while(temp !=
NULL && temp->next != NULL) temp = temp->next;
temp->next
= newNode;
cout<<("DATA INSERTED SUCCESSFULLY\n");
}}
void displayList()
{ struct node *temp;
if(head == NULL)
{
cout<<("List is empty.");
} else
{ temp = head;
while(temp !=
NULL) {
cout<<"Data
=" <<temp->data<<"\n";
temp =
temp->next; } }}
void deleteLastNode()
{ struct node
*toDelete, *secondLastNode;
if(head == NULL)
{
cout<<("List is already empty.");
} else
{ toDelete = head;
secondLastNode = head;
while(toDelete->next != NULL)
{
secondLastNode = toDelete;
toDelete =
toDelete->next;
}
if(toDelete ==
head) {
head =
NULL;
} else {
secondLastNode->next = NULL;
} free(toDelete);
cout<<("SUCCESSFULLY DELETED LAST NODE OF LIST\n");
}}
Input
Output
Practical 3
Aim-> multiplication of two matrix
Algorithm-> step1 start
Step2 multiply of the matrix
for(i=0; i<r;
i++)
{ for(j=0; j<c; j++)
{ mul[i][j]=0;
for(k=0;
k<c; k++)
{
mul[i][j]+=a[i][k]*b[k][j];
} } }
for(i=0; i<r;
i++)
{ for(j=0; j<c; j++)
{ cout<<mul[i][j]<<"
"; }
cout<<"\n"; }
Step3 stop
Code-> #include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ int
a[10][10],b[10][10],mul[10][10],r,c,i,j,k;
cout<<"enter the number of row=";
cin>>r;
cout<<"enter the number of column=";
cin>>c;
cout<<"enter the first matrix element=\n";
for(i=0; i<r;
i++)
{ for(j=0; j<c; j++)
{
cin>>a[i][j]; } }
cout<<"enter the second matrix element=\n";
for(i=0; i<r;
i++)
{ for(j=0; j<c; j++)
{ cin>>b[i][j]; } }
cout<<"multiply of the matrix=\n";
for(i=0; i<r;
i++)
{ for(j=0; j<c; j++)
{ mul[i][j]=0;
for(k=0;
k<c; k++)
{
mul[i][j]+=a[i][k]*b[k][j];} } }
for(i=0; i<r;
i++)
{ for(j=0; j<c; j++)
{ cout<<mul[i][j]<<"
"; }
cout<<"\n"; }
return 0;}
Input/output
Practical 4
Aim-> BFS program in c++
Algorithm step1 start
Step2 graph->for(i=1;
i<=max_edges; i++)
{Cout<<”\nEnter edge( -1 -1 to quit
)”<<i<<”:”;
Cin>>origin;
Cin>>destin;
If((origin == -1) && (destin == -1))
Break;
If(origin>=n || destin>=n || origin<0 ||
destin<0)
{Cout<<(“\nInvalid edge!\n”);
i--;}Else
{Adj[origin][destin] = 1;}}}
Step3insert_queue(int vertex)
{if(rear == MAX-1)
cout<<("\nQueue Overflow\n");
else
{if(front == -1)
front = 0;
rear = rear+1;
queue[rear] = vertex ;}}
Syep4delete_queue
if(front == -1 || front > rear)
{cout<<("\nQueue Underflow\n");
exit(1);}del_item = queue[front];
front = front+1;
return del_item;}
Step5 stop
Code->#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 100
#define initial 1
#define waiting 2
#define visited 3
int n;
int adj[MAX][MAX];
int state[MAX];
void create_graph();
void BF_Traversal();
void BFS(int v);
int queue[MAX], front = -1,rear = -1;
void insert_queue(int vertex);
int delete_queue();
int isEmpty_queue();
int main()
{create_graph();
BF_Traversal();
return 0;}void BF_Traversal()
{int v;
for(v=0; v<n; v++)
state[v] = initial;
cout<<("\nEnter starting vertex for Breadth First
Search : ");
cin>>(v);
BFS(v);
}void BFS(int v)
{int i;
insert_queue(v);
state[v] = waiting;
while(!isEmpty_queue())
{v = delete_queue( );
cout<<(v);
state[v] = visited;
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{if(adj[v][i] == 1 && state[i] == initial)
{insert_queue(i);
state[i] = waiting;}}}cout<<("\n");
}void insert_queue(int vertex)
{if(rear == MAX-1)
cout<<("\nQueue Overflow\n");
else
{if(front == -1)
front = 0;
rear = rear+1;
queue[rear] = vertex ;
}}int isEmpty_queue()
{if(front == -1 || front > rear)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}int delete_queue()
{int del_item;
if(front == -1 || front > rear)
{cout<<("\nQueue Underflow\n");
exit(1);
}del_item = queue[front];
front = front+1;
return del_item;
}void create_graph()
{int i,max_edges,origin,destin;
cout<<("\nEnter number of vertices : ");
cin>>(n);
max_edges = n*(n-1);
for(i=1; i<=max_edges; i++)
{cout<<"\nEnter edge( -1 -1 to quit
)"<<i<<":";
cin>>origin;
cin>>destin;
if((origin == -1) && (destin == -1))
break;
if(origin>=n || destin>=n || origin<0 ||
destin<0)
{cout<<("\nInvalid edge!\n");
i--;}else
{adj[origin][destin] = 1;}}}
Input/output
Practical 5
Aim-> DFS program in c++
Algorithm step1 start
Step2create_graphfor(i=1;i<=max_edges;i++)
{cout<<"\nEnter
edge( -1 -1 to quit )"<<i<<":";
cin>>origin;cin>>destin;
if( (origin == -1) && (destin == -1) )break;
if( origin >= n || destin >= n || origin<0 ||
destin<0)
{
cout<<("\nInvalid edge!\n");i--;}
else{adj[origin][destin]
= 1;}}}
Step3 while(!isEmpty_stack())
{ v = pop();
if(state[v]==initial)
{ cout<<(v);state[v]=visited;}for(i=n-1;
i>=0; i--) { if(adj[v][i]==1
&& state[i]==initial)
push(i);} }
Step4 stop
Code-> #include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 100
#define initial 1
#define visited 2
int n;
int adj[MAX][MAX];
int state[MAX];
void DF_Traversal();
void DFS(int v);
void create_graph();
int stack[MAX];
int top = -1;
void push(int v);
int pop();
int isEmpty_stack();
int main()
{create_graph();
DF_Traversal();}
void
DF_Traversal()
{ int v;
for(v=0; v<n; v++)
state[v]=initial;
cout<<("\nEnter starting node for Depth First
Search : ");
cin>>(v);
DFS(v);
cout<<
("\n");}
void DFS(int
v)
{int i;
push(v);
while(!isEmpty_stack())
{ v = pop();
if(state[v]==initial)
{
cout<<(v);
state[v]=visited;}
for(i=n-1;
i>=0; i--){
if(adj[v][i]==1
&& state[i]==initial) push(i); }}}
void push(int v)
{if(top == (MAX-1))
{
cout<<("\nStack Overflow\n");
return;}
top=top+1; stack[top] = v;}
int pop()
{ int v;
if(top == -1)
{
cout<<("\nStack Underflow\n");
exit(1);} else {
v = stack[top];
top=top-1; return v; }}
int
isEmpty_stack( )
{ if(top == -1)
return 1; else return
0;}
void create_graph()
{ int i,max_edges,origin,destin;
cout<<("\nEnter number of nodes :
");
cin>>(n);
max_edges=n*(n-1);
for(i=1;i<=max_edges;i++)
{cout<<"\nEnter edge( -1 -1 to quit
)"<<i<<":";
cin>>origin;cin>>destin;
if( (origin == -1) && (destin == -1) )break;
if( origin >= n || destin >= n || origin<0 ||
destin<0)
{
cout<<("\nInvalid edge!\n");i--;}
else{adj[origin][destin] = 1;}}}
Input/output
Practical 6
Aim ->Program for Minimum Spanning Tree using
Kruskal’s algorithm
Algorithm-> step1 start
Step2 for(i=0; i<n; i++)
father[i] = NIL;
while(
!isEmpty_pque( ) && count < n-1 )
{ tmp = del_pque();
v1 =
tmp->u;
v2 =
tmp->v;
while(
v1 !=NIL )
{ root_v1 = v1;
v1 = father[v1]; }
while(
v2 != NIL )
{ root_v2 = v2;
v2 = father[v2]; }
if(
root_v1 != root_v2 )
{ count++;
tree[count].u = tmp->u;
tree[count].v = tmp->v;
tree[count].weight = tmp->weight;
father[root_v2]=root_v1; }}
if(count <
n-1)
{ cout<<("\nGraph is not
connected, no spanning tree possible\n");
exit(1); }}
void insert_pque(int i,int j,int wt)
{ struct edge
*tmp,*q;
tmp = (struct
edge *)malloc(sizeof(struct edge));
tmp->u = i;
tmp->v = j;
tmp->weight
= wt;
if( front ==
NULL || tmp->weight < front->weight )
{ tmp->link = front;
front
= tmp; } else
{ q = front;
while( q->link != NULL
&& q->link->weight <= tmp->weight )
q = q->link;
tmp->link = q->link;
q->link = tmp;
if(q->link == NULL)
tmp->link = NULL; }}
struct edge *del_pque()
{ struct edge
*tmp;
tmp = front;
front =
front->link;
return tmp;}
int isEmpty_pque( )
{ if ( front ==
NULL )
return
1; else
return
0;}
Step3 for(i=1; i<=max_edges; i++)
{ cout<<"\nEnter
edge"<<i<<" (-1 -1 to quit): ";
cin>>origin>>destin;
if( (origin == -1)
&& (destin == -1) ) break;
cout<<("\nEnter weight for this edge : "); cin>>(wt);
if(
origin >= n || destin >= n || origin<0 || destin<0)
{ cout<<("\nInvalid
edge!\n");
i--; } else
insert_pque(origin,destin,wt); }};
Step4 for(i=0; i<n; i++)
father[i]
= NIL;
while(
!isEmpty_pque( ) && count < n-1 )
{ tmp = del_pque();
v1 =
tmp->u;
v2 =
tmp->v;
while(
v1 !=NIL )
{ root_v1 = v1;
v1 = father[v1]; }
while(
v2 != NIL )
{ root_v2 = v2;
v2 = father[v2]; }
if(
root_v1 != root_v2 )
{ count++;
tree[count].u = tmp->u;
tree[count].v = tmp->v;
tree[count].weight = tmp->weight;
father[root_v2]=root_v1; }}
if(count <
n-1)
{ cout<<("\nGraph is not
connected, no spanning tree possible\n");
exit(1); }}
void insert_pque(int i,int j,int wt)
{ struct edge
*tmp,*q;
tmp = (struct
edge *)malloc(sizeof(struct edge));
tmp->u = i;
tmp->v = j;
tmp->weight = wt;
if( front ==
NULL || tmp->weight < front->weight )
{ tmp->link = front;
front
= tmp; } else
{ q = front;
while(
q->link != NULL && q->link->weight <= tmp->weight )
q = q->link;
tmp->link = q->link;
q->link = tmp;
if(q->link == NULL)
tmp->link = NULL; }}
Step5 stop
Code-> #include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 100
#define NIL -1
struct edge
{ int u;
int v;
int weight;
struct edge
*link;
}*front = NULL;
void make_tree(struct edge tree[]);
void insert_pque(int i,int j,int wt);
struct edge *del_pque();
int isEmpty_pque( );
void create_graph();
int n;
int main()
{ int i;
struct edge
tree[MAX];
int wt_tree = 0;
create_graph();
make_tree(tree);
cout<<("\nEdges to be included in minimum spanning tree are
:\n");
for(i=1;
i<=n-1; i++)
{
cout<<tree[i].u<<"->";
cout<<tree[i].v<<"\n";
wt_tree += tree[i].weight; }
cout<<"\nWeight of this minimum spanning tree
is:\n"<<wt_tree;
return 0;}
void make_tree(struct edge tree[])
{ struct edge *tmp;
int
v1,v2,root_v1,root_v2;
int
father[MAX];
int i,count =
0;
for(i=0;
i<n; i++)
father[i] = NIL;
while(
!isEmpty_pque( ) && count < n-1 )
{ tmp = del_pque();
v1 =
tmp->u;
v2 =
tmp->v;
while(
v1 !=NIL )
{ root_v1 = v1;
v1 = father[v1]; }
while(
v2 != NIL )
{ root_v2 = v2;
v2 = father[v2]; }
if(
root_v1 != root_v2 )
{ count++;
tree[count].u = tmp->u;
tree[count].v = tmp->v;
tree[count].weight = tmp->weight;
father[root_v2]=root_v1; }}
if(count <
n-1)
{ cout<<("\nGraph is not
connected, no spanning tree possible\n");
exit(1); }}
void insert_pque(int i,int j,int wt)
{ struct edge
*tmp,*q;
tmp = (struct
edge *)malloc(sizeof(struct edge));
tmp->u = i;
tmp->v = j;
tmp->weight
= wt;
if( front ==
NULL || tmp->weight < front->weight )
{ tmp->link = front;
front
= tmp; } else
{ q = front;
while(
q->link != NULL && q->link->weight <= tmp->weight )
q = q->link;
tmp->link = q->link;
q->link = tmp;
if(q->link == NULL)
tmp->link = NULL; }}
struct edge *del_pque()
{ struct edge
*tmp;
tmp = front;
front =
front->link;
return tmp;}
int isEmpty_pque( )
{ if ( front ==
NULL )
return 1; else
return
0;}
void create_graph()
{ int
i,wt,max_edges,origin,destin;
cout<<("\nEnter number of vertices : ");
cin>>(n);
max_edges =
n*(n-1)/2;
for(i=1;
i<=max_edges; i++)
{ cout<<"\nEnter
edge"<<i<<" (-1 -1 to quit): ";
cin>>origin>>destin;
if( (origin
== -1) && (destin == -1) ) break;
cout<<("\nEnter weight for this edge : ") cin>>(wt); if( origin >= n || destin
>= n || origin<0 || destin<0) {
cout<<("\nInvalid
edge!\n");i--; } else
insert_pque(origin,destin,wt);}};
Input
Output
Practical 7
Aim-> chain multiplication program in c++
Algorithm-> step1 start
Step2 for (i=1; i<n; i++)
m[i][i] =
0;
for (L=2; L<n;
L++)
{ for (i=1; i<n-L+1; i++)
{ j= i+L-1;
m[i][j] =
INT_MAX;
for (k=i;
k<=j-1; k++)
{ q = m[i][k] + m[k+1][j] +
p[i-1]*p[k]*p[j];
if (q
< m[i][j])
{ m[i][j] = q;
} } }
}
return
m[1][n-1];
}
Step3 stop
Code->#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define INT_MAX m[1][n];
int MatrixChainMultiplication(int p[], int n)
{ int m[n][n];
int i, j, k, L, q;
for (i=1; i<n;
i++)
m[i][i] =
0;
for (L=2; L<n;
L++)
{ for (i=1; i<n-L+1; i++)
{ j= i+L-1;
m[i][j] =
INT_MAX;
for (k=i;
k<=j-1; k++)
{ q = m[i][k] + m[k+1][j] +
p[i-1]*p[k]*p[j];
if (q
< m[i][j])
{ m[i][j] = q;
} } }
}
return
m[1][n-1];
}
int main()
{ int n,i;
cout<<("Enter number of matrices\n");
cin>>(n);
n++;
int arr[n];
cout<<("Enter dimensions \n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ cout<<"Enter
d"<<i<<"=";
cin>>(arr[i]);
}
int size =
sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
cout<<"Minimum number of multiplications is
"<<MatrixChainMultiplication(arr, size);
return 0;
}
Input/output
Practical8
Aim->knapsack fractional program in c++
Algorithm->step1 start
Step2 for (i = 0; i < no_items; ++i)
used[i] =
0; cur_weight = capacity;
while (cur_weight
> 0)
{ item = -1;
for (i = 0; i < no_items; ++i)
if ((used[i] == 0)
&&
((item
== -1) || ((float) value[i] / weight[i] > (float) value[item] /
weight[item])))
item =
i; used[item] = 1;cur_weight -=
weight[item]; total_profit += value[item];
if (cur_weight >= 0)
Step3 int item_percent = (int) ((1 + (float) cur_weight /
weight[item]) * 100);
cout<<"Addedobject in the bag="<<item +
1<<"\n"<<"profit="<<value[item]<<"\n"<<"weight="<<weight[item]<<"\n";
total_profit -= value[item];
total_profit += (1 + (float)cur_weight / weight[item]) * value[item];
Step4 stop
Code->#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ int capacity,
no_items, cur_weight, item;
int used[10];
float
total_profit;
int i;
int weight[10];
int value[10];
cout<<("Enter the capacity of knapsack:\n");
cin>>(capacity);
cout<<("Enter the number of items:\n");
cin>>(no_items); cout<<"Enter
the weight and value of "<<no_items<<"item:\n";
for (i = 0; i <
no_items; i++)
{ cout<<"Weight
"<<i<<"th item"<<"="; cin>>weight[i]; cout<<"value
"<<i<<"th item"<<"="; cin>>value[i]; }
for (i = 0; i < no_items; ++i)
used[i] = 0; cur_weight =
capacity; while (cur_weight >
0) { item = -1; for (i = 0; i < no_items; ++i)
if
((used[i] == 0) &&
((item == -1) || ((float) value[i] / weight[i] > (float) value[item]
/ weight[item]))) item =
i; used[item] = 1; cur_weight -= weight[item]; total_profit += value[item]; if (cur_weight >= 0) cout<<"Added
object="<<item + 1<<"\n"<<"profit="<<value[item]<<"\n"<<"weight="<<weight[item]<<"\n"<<"completely
in the bag Space left="<<cur_weight<<"\n"; else {
int
item_percent = (int) ((1 + (float) cur_weight / weight[item]) * 100); cout<<"Addedobject in
the bag="<<item + 1<<"\n"<<"profit="<<value[item]<<"\n"<<"weight="<<weight[item]<<"\n"; total_profit -= value[item]; total_profit += (1 + (float)cur_weight
/ weight[item]) * value[item]; } }
cout<<"Filled the bag with objects total
Profit.\n"<<total_profit;}
Input/output
Practical9
Aim->prim’s program in c++
Algorithm->step1 start
Step2 for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{ predecessor[i] = NIL;
length[i] = infinity;
status[i] = TEMP; }
length[r] = 0;
Step3 for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{ if(status[i] == TEMP && length[i]
< min)
{ min = length[i];
k = i;
Step4 for(i=0; i<n; i++)
if(adj[current][i]>0&&status[i] == TEMP) if(adj[current][i]<length[i]){ predecessor[i]=current;
length[i]=adj[current][i];
Step5 stop
Code #include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 10
#define TEMP 0
#define PERM 1
#define infinity 9999
#define NIL -1
struct edge
{ int u;
int v;
};
int n;
int adj[MAX][MAX];
int predecessor[MAX];
int status[MAX];
int length[MAX];
void create_graph();
void maketree(int r, struct edge tree[MAX]);
int min_temp();
int main()
{ int wt_tree =
0;
int i, root;
struct edge tree[MAX];
create_graph();
cout<<("\nEnter root vertex : ");
cin>>(root);
maketree(root,
tree);
cout<<("\nEdges to be included in spanning tree are :
\n");
for(i=1;
i<=n-1; i++)
{ cout<<tree[i].u<<"->"<<tree[i].v<<"\n";
wt_tree += adj[tree[i].u][tree[i].v];
}
cout<<"\nWeight of spanning tree is :" <<wt_tree;
return 0;}
void maketree(int r, struct edge tree[MAX])
{ int current,i;
int count = 0;
for(i=0;
i<n; i++)
{ predecessor[i] = NIL;
length[i] = infinity;
status[i] = TEMP; }
length[r] = 0;
while(1)
{ current = min_temp();
if(current
== NIL)
{ if(count == n-1)
return;
else
{ cout<<("\nGraph is
not connected, No spanning tree possible\n");
exit(1); } }
status[current] = PERM;
if(current != r)
{
count++;
tree[count].u = predecessor[current];
tree[count].v = current;
} for(i=0; i<n; i++)
if(adj[current][i] > 0 && status[i] == TEMP)
if(adj[current][i] < length[i])
{ predecessor[i] = current;
length[i]
= adj[current][i];
}}}
int min_temp()
{ int i;
int min =
infinity;
int k = -1;
for(i=0;
i<n; i++)
{ if(status[i] == TEMP && length[i]
< min)
{ min = length[i];
k = i; } }
return k;}
void create_graph()
{ int
i,max_edges,origin,destin,wt;
cout<<("\nEnter number of vertices : ");
cin>>(n);
max_edges =
n*(n-1)/2;
for(i=1; i<=max_edges; i++)
{ cout<<"\nEnter edge
"<<i<<"(-1 -1 to quit) : ";
cin>>origin>>destin;
if((origin == -1) && (destin == -1))
break;
cout<<("\nEnter weight for this edge : ");
cin>>(wt);
if(
origin >= n || destin >= n || origin < 0 || destin < 0)
{ cout<<("\nInvalid
edge!\n");
i--;
}
else
{
adj[origin][destin] = wt;
adj[destin][origin] = wt;
} }}
Input/output











Comments
Post a Comment