Data structure notes (DS)
Note remember page numbers
Data Structures (DS) tutorial provides basic and advanced concepts of Data Structure. Our Data Structure tutorial is designed for beginners and professionals.
Data Structure is a way to store and organize data so that it can be used efficiently.
Our Data Structure tutorial includes all topics of Data Structure such as Array, Pointer, Structure, Linked List, Stack, Queue, Graph, Searching, Sorting, Programs, etc.
What is Data Structure?
The data structure name indicates itself that organizing the data in memory. There are many ways of organizing the data in the memory as we have already seen one of the data structures, i.e., array in C language. Array is a collection of memory elements in which data is stored sequentially, i.e., one after another. In other words, we can say that array stores the elements in a continuous manner. This organization of data is done with the help of an array of data structures. There are also other ways to organize the data in memory. Let's see the different types of data structures.
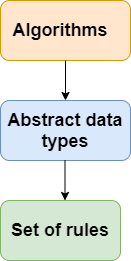
The data structure is not any programming language like C, C++, java, etc. It is a set of algorithms that we can use in any programming language to structure the data in the memory.
To structure the data in memory, 'n' number of algorithms were proposed, and all these algorithms are known as Abstract data types. These abstract data types are the set of rules.
Types of Data Structures
There are two types of data structures:
- Primitive data structure
- Non-primitive data structure
Primitive Data structure
The primitive data structures are primitive data types. The int, char, float, double, and pointer are the primitive data structures that can hold a single value.
Non-Primitive Data structure
There are two types of data structures:
- Primitive data structure
- Non-primitive data structure
Primitive Data structure
The primitive data structures are primitive data types. The int, char, float, double, and pointer are the primitive data structures that can hold a single value.
Non-Primitive Data structure
The non-primitive data structure is divided into two types:
- Linear data structure
- Non-linear data structure
Linear Data Structure
The arrangement of data in a sequential manner is known as a linear data structure. The data structures used for this purpose are Arrays, Linked list, Stacks, and Queues. In these data structures, one element is connected to only one another element in a linear form.
When one element is connected to the 'n' number of elements known as a non-linear data structure. The best example is trees and graphs. In this case, the elements are arranged in a random manner.
We will discuss the above data structures in brief in the coming topics. Now, we will see the common operations that we can perform on these data structures.
Data structures can also be classified as:
- Static data structure: It is a type of data structure where the size is allocated at the compile time. Therefore, the maximum size is fixed.
- Dynamic data structure: It is a type of data structure where the size is allocated at the run time. Therefore, the maximum size is flexible.
Major Operations
The major or the common operations that can be performed on the data structures are:
- Searching: We can search for any element in a data structure.
- Sorting: We can sort the elements of a data structure either in an ascending or descending order.
- Insertion: We can also insert the new element in a data structure.
- Updation: We can also update the element, i.e., we can replace the element with another element.
- Deletion: We can also perform the delete operation to remove the element from the data structure.
Which Data Structure?
A data structure is a way of organizing the data so that it can be used efficiently. Here, we have used the word efficiently, which in terms of both the space and time. For example, a stack is an ADT (Abstract data type) which uses either arrays or linked list data structure for the implementation. Therefore, we conclude that we require some data structure to implement a particular ADT.
An ADT tells what is to be done and data structure tells how it is to be done. In other words, we can say that ADT gives us the blueprint while data structure provides the implementation part. Now the question arises: how can one get to know which data structure to be used for a particular ADT?.
As the different data structures can be implemented in a particular ADT, but the different implementations are compared for time and space. For example, the Stack ADT can be implemented by both Arrays and linked list. Suppose the array is providing time efficiency while the linked list is providing space efficiency, so the one which is the best suited for the current user's requirements will be selected.
Advantages of Data structures
Accessing Structure Members
To access any member of a structure, we use the member access operator (.). The member access operator is coded as a period between the structure variable name and the structure member that we wish to access. You would use struct keyword to define variables of structure type. Following is the example to explain usage of structure
Structures are used to represent a record, suppose you want to keep track of your books in a library. You might want to track the following attributes about each book −
- Title
- Author
- Subject
- Book ID
Defining a Structure
To define a structure, you must use the struct statement. The struct statement defines a new data type, with more than one member, for your program. The format of the struct statement is this −
struct [structure tag] {
member definition;
member definition;
...
member definition;
} [one or more structure variables];
The structure tag is optional and each member definition is a normal variable definition, such as int i; or float f; or any other valid variable definition. At the end of the structure's definition, before the final semicolon, you can specify one or more structure variables but it is optional. Here is the way you would declare the Book structure −
struct Books {
char title[50];
char author[50];
char subject[100];
int book_id;
} book; C/C++ arrays allow you to define variables that combine several data items of the same kind, but structure is another user defined data type which allows you to combine data items of different kinds.
Structures are used to represent a record, suppose you want to keep track of your books in a library. You might want to track the following attributes about each book −
Title
Author
Subject
Book ID
Defining a Structure
To define a structure, you must use the struct statement. The struct statement defines a new data type, with more than one member, for your program. The format of the struct statement is this






























Comments
Post a Comment